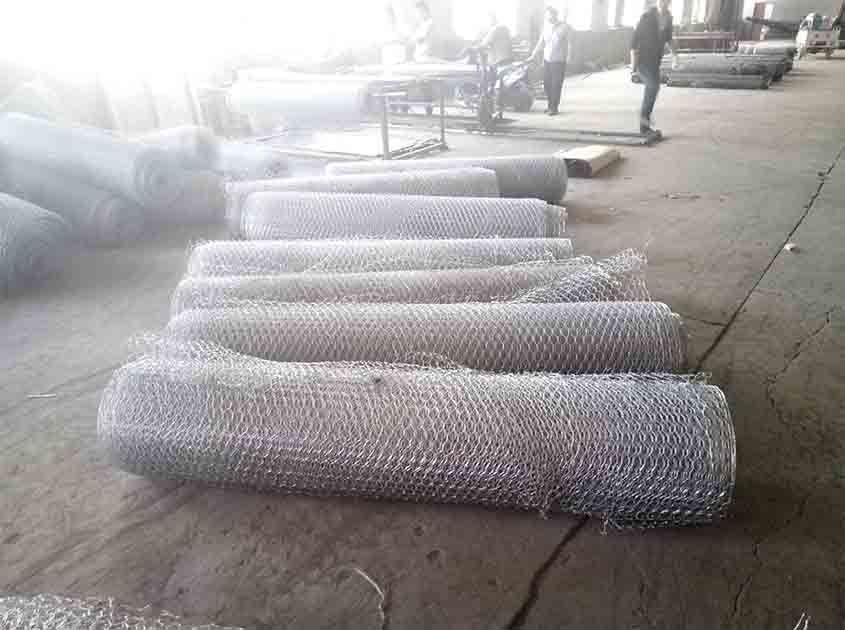
Is chicken wire mesh resistant to corrosion and rust
Chicken wire mesh, also known as poultry netting, is a widely used fencing material due to its affordability and versatility. However, concerns about its resistance to corrosion and rust may arise, especially when considering long-term durability. In this article, we will delve into the topic and examine the factors that affect the corrosion and rust resistance of chicken wire mesh, providing insights into its performance and maintenance requirements.

Understanding Chicken Wire Mesh Composition:
Chicken wire mesh is typically made from galvanized steel wire. Galvanization is a process where a layer of zinc is applied to the steel wire to provide corrosion resistance. The galvanization process forms a protective barrier that prevents the steel from direct exposure to corrosive elements, such as moisture and oxygen.

Corrosion and Rust Resistance:
Galvanized Chicken Wire Mesh: The galvanized coating on chicken wire mesh significantly enhances its resistance to corrosion and rust. The zinc layer acts as a sacrificial barrier, corroding before the steel wire does. This sacrificial nature of zinc helps protect the underlying steel, extending the lifespan of the chicken wire mesh. Galvanized chicken wire mesh is widely used in various applications, including poultry enclosures, garden fencing, and agricultural fencing, due to its superior corrosion resistance.

Environmental Factors:
While galvanized chicken wire mesh is designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions, its resistance to corrosion and rust can still be influenced by external factors. Factors such as exposure to saltwater, high humidity, acidic or alkaline environments, and pollutants can accelerate the corrosion process. In coastal areas or locations with high levels of air pollution, stainless steel chicken wire mesh may be a better choice, as it offers enhanced resistance to corrosion and rust.
-
 Best Welded Wire Mesh for South American Markets Feb 03, 2026
Best Welded Wire Mesh for South American Markets Feb 03, 2026 Why Galvanized Wire Mesh Is Popular in South America Jan 26, 2026
Why Galvanized Wire Mesh Is Popular in South America Jan 26, 2026 How to Check the Quality of Welded Wire Mesh Jan 16, 2026
How to Check the Quality of Welded Wire Mesh Jan 16, 2026
- Tel.: +86 311 83077076
- E-mail: sales@qunkunmetal.com
- Skype: qunkunsales01
- WhatsApp: 8618032412189
- Add.: No.69 The Filter Industrial Part of Anping, Hebei, China


















